Labeling Rule Examples
This section provides several detailed examples of crafting labeling rules.
Keep in mind the following as you craft labeling rules:
The operator you select and the particular values you enter in the Values field allow you to control the granularity of the labeling rule.
When you include multiple statements in a condition, Rule-Based Labeling automatically inserts an AND between the statements.
When you specify multiple values in a statement, Rule-Based Labeling automatically inserts an OR between the values.
Example 1. Hostname Rule to match workloads that contain part of a specified host name
Select Hostname in the Attribute field.
Select contains in the Operator field.
Enter AWS in the Values field.
Click Close.
Select one or more labels in the Label field.
Click Save.
Example 2. OS Rule to match workloads running a specific operating system
Note
You can configure OS labeling rules to match all or part of the workload's OS version or release by selecting operators and entering the details. To find details, go to Servers & Endpoints > Workloads and click the workload. On the Summary tab, go to the Attributes section of the workload's details page.
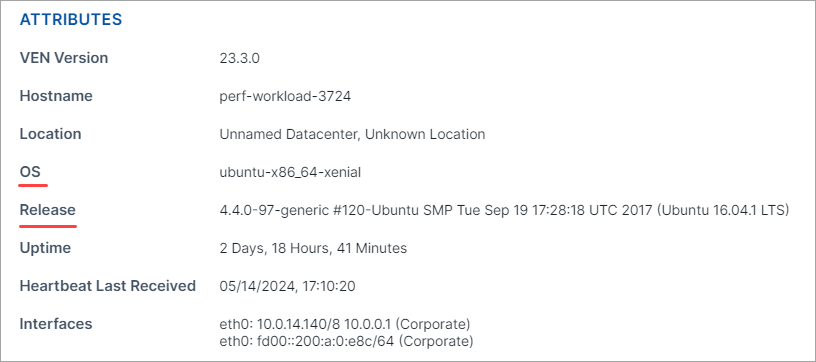
Select OS in the Attribute field.
Select an Operator.
Select Linux in the Value field.
Click Close.
Select one or more labels in the Label field.
Click Save.
Example 3. IP Address Rule to match workloads within a specific IP address range:
Select IP Address in the Attribute field.
Select is in in the Operator field.
In the Value field, enter a narrow range such as
10.2.0.0 - 10.2.200.0.Click Close.
Select one or more labels in the Label field.
Click Save.
Example 4. CIDR Block Rule to match workloads within a specific CIDR block:
Select IP Address in the Attribute field.
Select is in in the Operator field.
In the Value field, enter a CIDR block. For example:
10.2.20.0/24Click Close.
Select one or more labels in the Label field.
Click Save.
Example 5. Rule with multiple attributes, each with a single value:
Specify a hostname:
Select Hostname in the Attribute field.
Select contains in the Operator field.
Enter details in the Values field.
Specify an operating system:
Select OS in the Attribute field.
Select contains in the Operator field.
Select an operating system in the Values field.
Specify an IP address:
Select IP Address in the Attribute field.
Select is in in the Operator field.
In the Values, field enter an IP range or CIDR block.
Specify a listening port and/or protocol:
Select Port/Protocol in the Attribute field.
In the Operator field, select is for a specific port/protocol; select is in to specify a range.
In the Values field, enter either a specific port/protocol or a range as appropriate.
Specify a process path:
Select Process in the Attribute field.
In the Operator field, select an appropriate operator.
In the Values field, enter all or part of a process path according to your selected operator.
Click Close.
Select one or more labels in the Label field.
Click Save.